Midwestern University Researcher discovers new Insight into Early Human Migration
New face reconstruction from Ethiopia provides a new vision of the origins and early migration of human ancestors.
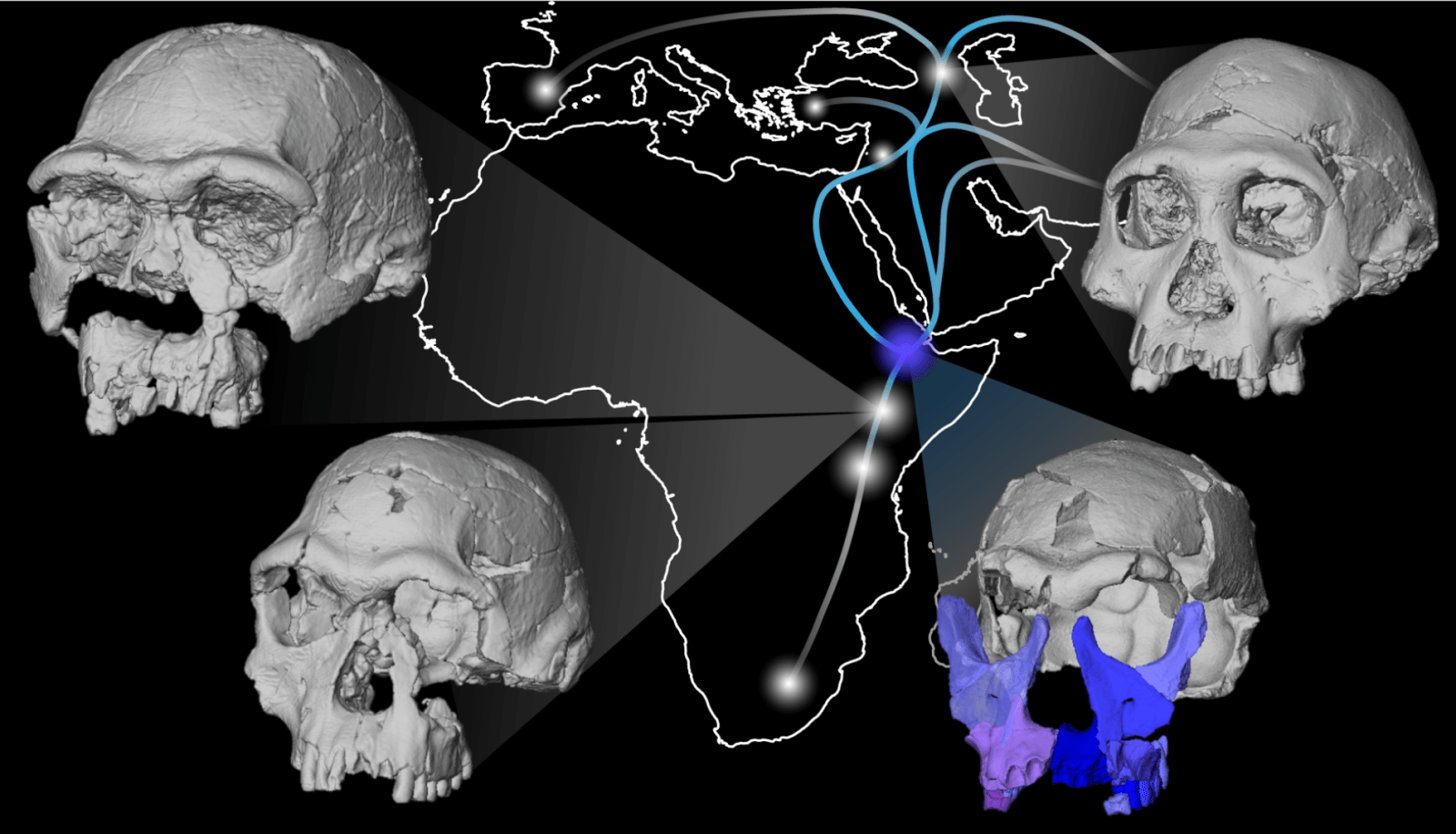
A 1.5-million-year-old fossil from Gona, Ethiopia reveals new details about the first hominin species to disperse from Africa.
Summary: Virtual reassembly of teeth and fossil bone fragments reveals a beautifully preserved face of a 1.5-million-year-old human ancestor—the first complete Early Pleistocene hominin cranium from the Horn of Africa. This fossil, from Gona, Ethiopia, hints at a surprisingly archaic face in the earliest human ancestors to migrate out of Africa.
A team of international scientists, led by Dr. Karen Baab, a paleoanthropologist at the College of Graduate Studies, Glendale Campus of Midwestern University in Arizona, produced a virtual reconstruction of the face of early Homo erectus. The 1.5 to 1.6 million-year-old fossil, called DAN5, was found at the site of Gona, in the Afar region of Ethiopia. This surprisingly archaic face yields new insights into the first species to spread across Africa and Eurasia. The team’s findings are being published in Nature Communications.
According to Dr. Baab, “We already knew that the DAN5 fossil had a small brain, but this new reconstruction shows that the face is also more primitive than classic African Homo erectus of the same antiquity. One explanation is that the Gona population retained the anatomy of the population that originally migrated out of Africa approximately 300,000 years earlier.”
The Gona Paleoanthropological Research Project in the Afar of Ethiopia is co-directed by Dr. Sileshi Semaw (Centro Nacional de Investigación sobre la Evolución Humana, Spain) and Dr. Michael Rogers (Southern Connecticut State University). Gona has yielded hominin fossils that are older than 6.3 million years ago, and stone tools spanning the last 2.6 million years of human evolution. The newly presented hominin reconstruction includes a fossil brain case (previously described in 2020) and smaller fragments of the face belonging to a single individual called DAN5 dated to between 1.6 and 1.5 million years ago. The face fragments (and teeth) have now been reassembled using virtual techniques to generate the most complete skull of a fossil human from the Horn of Africa in this time period. The DAN5 fossil is assigned to Homo erectus, a long-lived species found throughout Africa, Asia, and Europe after approximately 1.8 million years ago.
The researchers used high-resolution micro-CT scans of the four major fragments of the face, which were recovered during the 2000 fieldwork at Gona. 3D models of the fragments were generated from the CT scans. The face fragments were then re-pieced together on a computer screen, and the teeth were fit into the upper jaw where possible. The final step was “attaching” the face to the braincase to produce a mostly complete cranium. This reconstruction took about a year and went through several iterations before arriving at the final version.
Dr. Baab, who was responsible for the reconstruction, described this as “a very complicated 3D puzzle, and one where you do not know the exact outcome in advance. Fortunately, we do know how faces fit together in general, so we were not starting from scratch.”
This new study shows that the Gona population 1.5 million years ago had a mix of typical Homo erectus characters concentrated in its braincase, but more ancestral features of the face and teeth normally only seen in earlier species. For example, the bridge of the nose is quite flat, and the molars are large. Scientists determined this by comparing the size and shape of the DAN5 face and teeth with other fossils of the same geological age, as well as older and younger ones. A similar combination of traits was documented previously in Eurasia, but this is the first fossil to show this combination of traits inside Africa, challenging the idea that Homo erectus evolved outside of the continent. “I'll never forget the shock I felt when Dr. Baab first showed me the reconstructed face and jaw,” says Dr. Yousuke Kaifu of the University of Tokyo, a co-author of the study.
“The oldest fossils belonging to Homo erectus are from Africa, and the new fossil reconstruction shows that transitional fossils also existed there, so it makes sense that this species emerged on the African continent,” says Dr. Baab. “But the DAN5 fossil postdates the initial exit from Africa, so other interpretations are possible.”
Dr. Rogers agrees. “This newly reconstructed cranium further emphasizes the anatomical diversity seen in early members of our genus, which is only likely to increase with future discoveries.”
“It is remarkable that the DAN5 Homo erectus was making both simple Oldowan stone tools and early Acheulian handaxes, among the earliest evidence for the two stone tool traditions to be found directly associated with a hominin fossil,” adds Dr. Semaw.
The researchers are hoping to compare this fossil to the earliest human fossils from Europe, including fossils assigned to Homo erectus but also a distinct species, Homo antecessor, both dated to approximately one million years ago. "Comparing DAN5 to these fossils will not only deepen our understanding of facial variability within Homo erectus but also shed light on how the species adapted and evolved," explains Dr. Sarah Freidline of the University of Central Florida, study co-author.
There is also potential to test alternative evolutionary scenarios, such as genetic admixture between two species, as seen in later human evolution among Neanderthals, modern humans and “Denisovans.” For example, maybe DAN5 represents the result of admixture between classic African Homo erectus and the earlier Homo habilis species. According to Dr. Rogers, “We’re going to need several more fossils dated between one to two million years ago to sort this out.”
Main Image:
Fossil fragments of a face as well as teeth were reassembled to produce the most complete cranium of a human ancestor from this time in the Horn of Africa.
An international research effort led by Midwestern University faculty researcher Karen Baab, Ph.D., Professor, Anatomy, College of Graduate Studies, Glendale Campus, has utilized a remarkably preserved 1.5-million-year-old fossil face to help expand scientists’ understanding of early human evolution and migration. The study, published in Nature Communications, presents the first complete Early Pleistocene hominin cranium from the Horn of Africa and is based on a fossil discovered at the Gona archaeological site in Ethiopia.
Using high-resolution micro-CT scanning and advanced virtual reconstruction techniques, the international research team created a virtual cranial reassembly based on facial and dental fragments belonging to an early Homo erectus individual known as DAN5. The reconstructed face shows a combination of features - an archaic facial structure paired with more derived braincase traits - that challenges long-standing assumptions about where and how Homo erectus evolved before dispersing beyond Africa.
Since its publication, the findings are gaining widespread attention within the scientific community, contributing to ongoing discussions about anatomical diversity and evolutionary transitions among early members of the human lineage.
