For almost 80 years, 22 artifacts from Okinawa, Japan were lost to history, only to be discovered last year, tucked away in an attic of a private residence in Massachusetts.
Now, thanks to an investigation led by the FBI—with support from the Department of Defense and the Smithsonian Institution—these artifacts have returned home.
The FBI began investigating the case in January 2023. Special Agent Geoffrey J. Kelly of the FBI Boston Field Office received a complaint from a family that found some unique items while sorting through their deceased father’s belongings. Their father was a World War II veteran, but never served in the Pacific Theater.
“They came across some what appeared to be very valuable Asian art,” said Kelly, who is the art crime coordinator for FBI Boston and a member of the FBI Art Crime Team. “There were some scrolls, there were some pottery pieces, there was an ancient map. They looked old and valuable. And because of this, they did a little research and they determined that at least the scrolls had been entered about 20 years ago in the FBI's National Stolen Art File.”
The National Stolen Art File is the repository for stolen art in the U.S. and abroad that is searchable by the public and law enforcement to help people identify items of stolen art and/or antiquities and other types of items. Important documents and treasures of the Ryukyu Kingdom were taken during the World War II Battle of Okinawa. In 2001 the Prefectural Board of Education in Japan, as a result of participation in the Department of State’s International Visitor Leadership Program, had registered many of these missing articles with the National Stolen Art File.
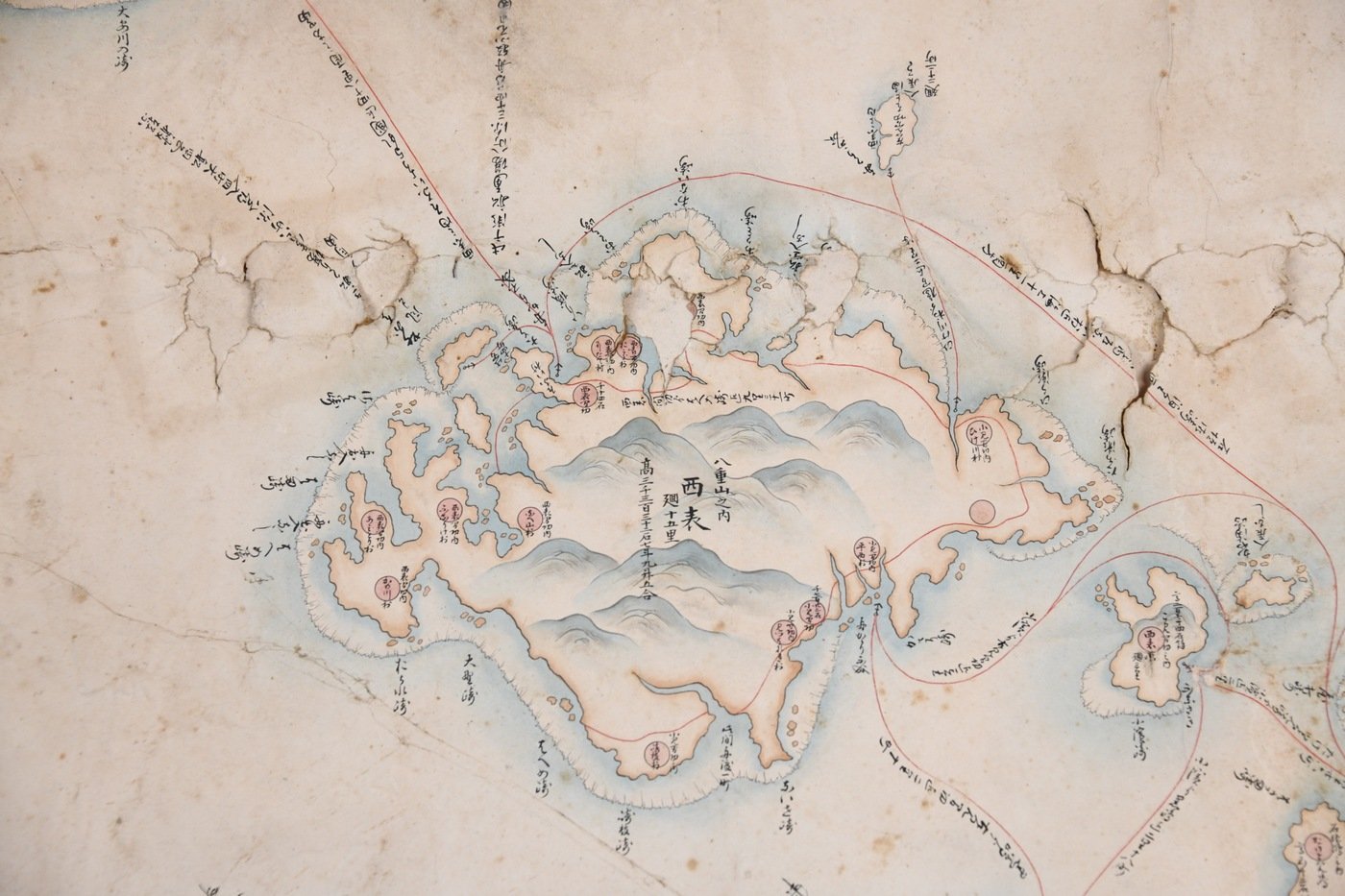
In total, the FBI recovered 22 artifacts: six painted scrolls from the 18th-19th centuries (three of which were one piece and appear to have been divided into three pieces), a hand-drawn map of Okinawa dating back to the 19th century, and various pieces of pottery and ceramics. A typewritten letter was also found with the artifacts in Massachusetts that helped confirm they were looted during the last days of World War II.
“When taken together, they really represent a substantial piece of Okinawan history,” said Kelly.
The FBI transported the artifacts from Massachusetts to Smithsonian Institution's National Museum of Asian Art in Washington, D.C., where the scrolls were unfurled for the first time in many years, revealing portraits of Okinawan royalty in vivid reds, golds, and blue accents.
“It's an exciting moment when you when you watch the scroll unfurl in front of you,” said Kelly. “You witness history, and you witness something that hasn't been seen by many people in a very long time.”
Kelly explained that these artifacts were especially important because they depict Okinawan royalty—and serve as pieces of cultural identity. "A nation's cultural identity is really summed up in the artifacts and the history,” said Kelly. “This is what makes a culture. And without it, you're taking away their history. And the surest way to eliminate a culture is to eliminate their past. And so, it's really important for us as stewards of artifacts and cultural patrimony to make every effort that we can to see that these go back to the civilizations and the cultures in the countries where they belong.”
The National Museum of Asian Art assisted the FBI in ensuring that the artifacts were properly packaged for transport. Colonel Scott DeJesse and U.S. Army Civil Affairs & Psychological Operations Command (Airborne) 38 G Monuments Men and Women led the effort to secure and transport the artifacts to Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. The Naval Criminal Investigative Service provided additional support, and FBI legal attaché office in Tokyo was responsible for the handover of the artifacts in Japan. On March 15, 2024, the official handover took place, and Denny Tamaki, the Governor of Okinawa Prefecture, announced the return of the artifacts.
Main Image :A hand-drawn map of Okinawa dating back to the 19-th century